Next: 8.3 Exponential Map Up: 8 SO(3) Previous: 8.1 Description
The Lie algebra
![]() is the set of antisymmetric
is the set of antisymmetric
![]() matrices, generated by the differential rotations about
each axis:
matrices, generated by the differential rotations about
each axis:
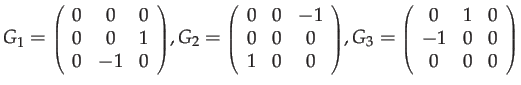 |
(95) |
The mapping
![]() sends 3-vectors to their skew matrix:
sends 3-vectors to their skew matrix:
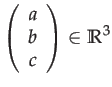 |
(96) | ||
| (97) | |||
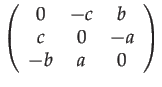 |
(98) |